Rangeland diversity as a forage resource for wild ungulates in the Barsa Kelmes nature reserve (Kazakhstan)
Authors: Dimeyeva L.A., Salmukhanbetova Z. K., Malakhov D.V., Wunderlich J.
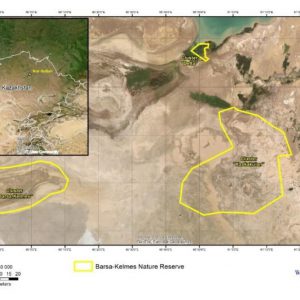
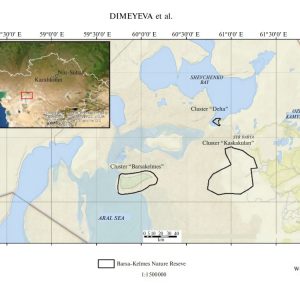
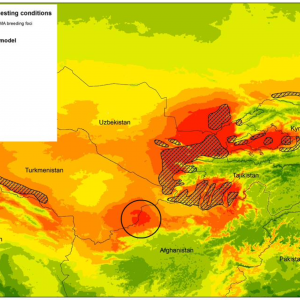
Abstract: The nature reserve was founded in 1939 in the limits of the Barsa Kelmes Island (the Aral Sea, Kazakhstan) for the conservation of the saiga antelope (Saiga tatarica) and goitered gazelle (Gazella subgutturosa). In 1953 kulan from Turkmenistan (Equus hemionus kulan) were introduced to the island.